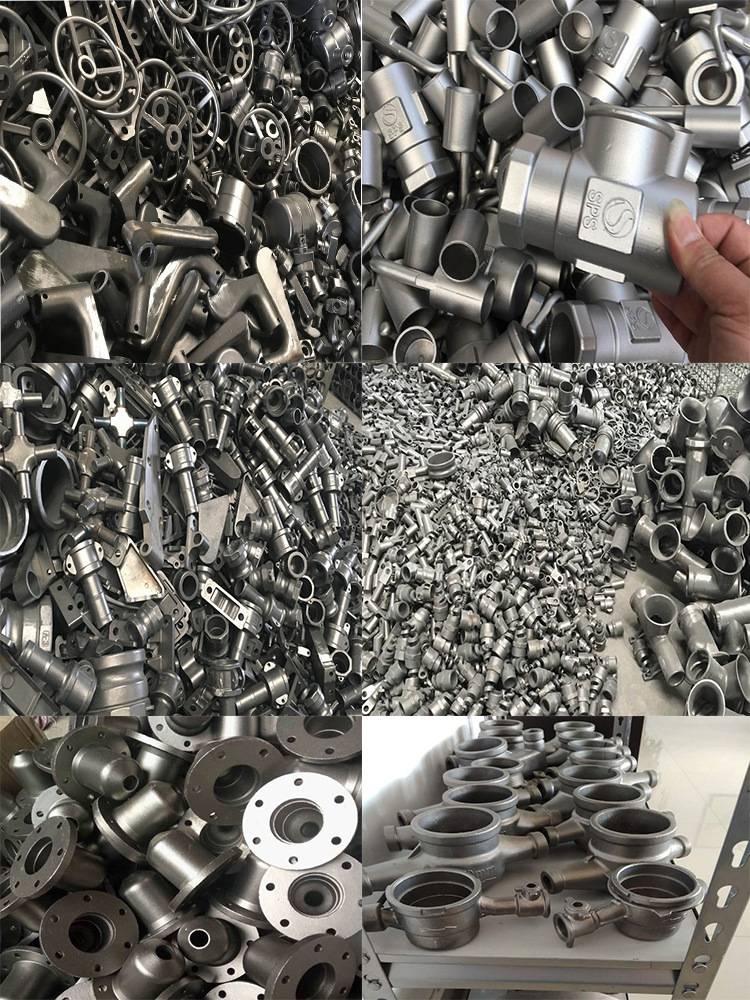
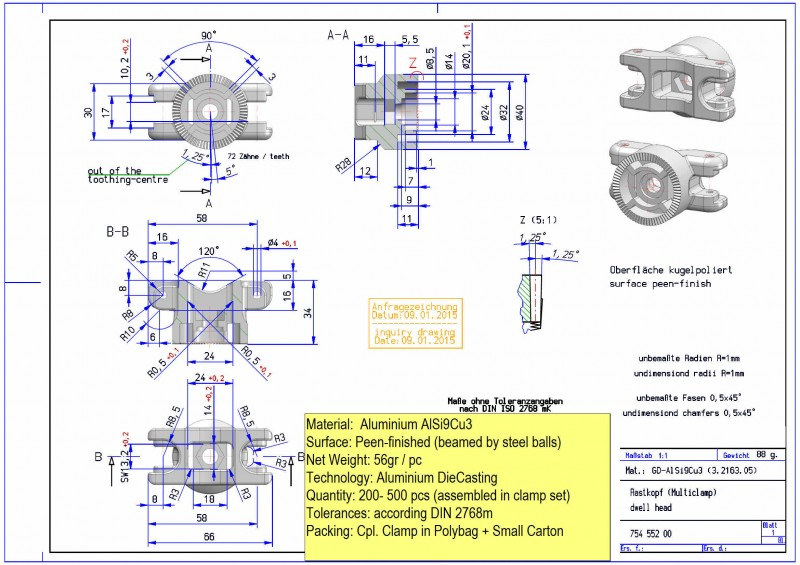
Componenti fusi
I getti sono oggetti metallici formati ottenuti attraverso vari metodi di fusione. In altre parole, il metallo liquido, dopo essere stato fuso, viene versato, iniettato, aspirato o colato in uno stampo preparato in anticipo. Dopo il raffreddamento e ulteriori lavorazioni come la smerigliatura, si ottiene un oggetto con una forma, dimensioni e proprietà specifiche.
I getti possono essere classificati in vari modi: in base al materiale metallico utilizzato, si dividono in getti d'acciaio, getti di ghisa, getti di rame, getti di alluminio, getti di magnesio, getti di zinco, getti di titanio, ecc. Ogni tipo di getto può essere ulteriormente suddiviso in base alla sua composizione chimica o alla struttura metallografica. Ad esempio, i getti di ghisa possono essere classificati in getti di ghisa grigia, getti di ghisa sferoidale, getti di ghisa vermicolare, getti di ghisa malleabile e getti di ghisa legata. In base al metodo di formatura dello stampo, i getti possono essere suddivisi in getti in stampi di sabbia, getti in stampi metallici, getti a pressione (pressofusione), getti centrifugati, getti a colata continua, getti a cera persa, getti in stampi ceramici, getti per rifusione elettroslag e getti bimetallici. Tra questi, i getti in stampi di sabbia sono i più utilizzati, rappresentando circa l'80% della produzione totale di getti. I getti in metalli non ferrosi come alluminio, magnesio e zinco sono spesso realizzati mediante pressofusione.
Castings are metal forming objects obtained by various casting methods, that is, the smelted liquid metal is injected into the pre-prepared casting mold by pouring, injection, suction or other casting methods, and after cooling, it is polished and other subsequent processing methods to obtain an object with a certain shape, size and performance.
There are many classification methods for castings: according to the different metal materials used, they are divided into steel castings, iron castings, copper castings, aluminum castings, magnesium castings, zinc castings, titanium castings, etc. Each type of casting can be further divided into different types according to its chemical composition or metallographic structure. For example, iron castings can be divided into gray iron castings, ductile iron castings, compacted graphite iron castings, malleable iron castings, alloy iron castings, etc.; According to the different casting molding methods, castings can be divided into ordinary sand castings, metal castings, die castings, centrifugal castings, continuous castings, investment castings, ceramic castings, electroslag remelting castings, bimetal castings, etc. Among them, ordinary sand castings are the most widely used, accounting for about 80% of the total casting output. Non-ferrous metal castings such as aluminum, magnesium, and zinc are mostly die castings.