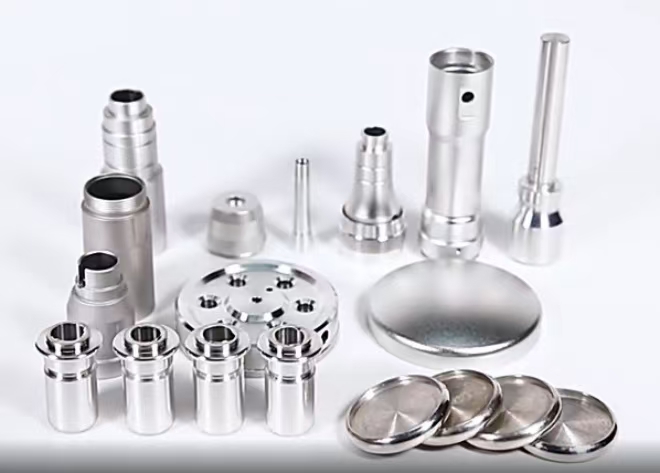
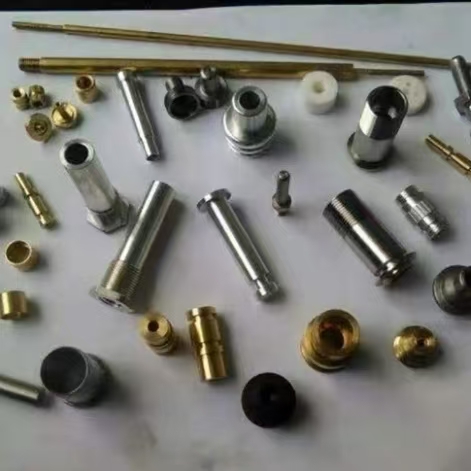
lingot di ferro ad alta purezza presenta i vantaggi di basso contenuto di zolfo, basso contenuto di fosforo e alta purezza, ed è stato ampiamente utilizzato come materiale per la rimoltenza nella produzione di leghe precise, leghe termoelettriche, leghe magnetiche dure e acciai inossidabili a basso carbonio, e può essere utilizzato come materia prima per la produzione di polveri metallurgiche. È particolarmente adatto per la produzione di superleghe e magneti permanenti NdFeB ad alta potenza e così via.
Applicazioni:
Il ferro puro per la fusione viene ampiamente utilizzato nella produzione di vari tipi di leghe speciali, come leghe intermedie, leghe termoelettriche, leghe magnetiche dure, acciai inossidabili a basso carbonio e materiali per la metallurgia a polvere.
High-purity iron billet has the advantages of low sulfur, low phosphorus and high purity, and has been widely used as a material for remelting the production of precision alloys, electric heating alloys, hard magnetic alloys, and low-carbon stainless steels, and can be used as raw materials for the production of metallurgical powders, especially suitable for the production of ultra-high alloys and high-energy grade NdFeB permanent magnets.
Apply:
1. Pure iron for melting is widely used in the production of various types of special alloys, such as intermediate alloys, electric heating alloys, hard magnetic alloys, low carbon stainless steels and powder metallurgy materials.


Ferro puro per materiali magnetici
Il ferro ad alta purezza è adatto per la produzione di materiali magnetici, come magneti ferritici, magneti permanenti NdFeB e così via, ed è ampiamente utilizzato nei campi elettronico, meccanico dell'elettricità, apparecchiature mediche e così via. Giocattoli, confezionamento, artigianato in metallo, aerospazio e così via.
Il magnete NdFeB di ramee della terza generazione è il magnete permanente più potente attualmente. È costituito da neodimio (Nd), un metallo di ramee (29% - 32,5%), ferro (Fe) (63,95% - 68,65%), boro (B), un elemento non metallico, e altri additivi, come dysprosio (Dy) (0,6% - 8%), niobio (Nb) (0,3% - 0,5%), alluminio (Al) (0,3% - 0,5%), rame (Cu) (0,05% - 0,15%) e così via.
2. Pure iron for magnetic materials
High-purity iron is suitable for the production of magnetic materials, such as ferrite magnets, NdFeB permanent magnets, etc., which are widely used in electronics, power machinery, medical equipment and other fields. Toys, packaging, hardware mechanics, aerospace, etc.
The third-generation rare earth NdFeB magnet is the most powerful permanent magnet at present, which is composed of rare earth metals neodymium (29%-32.5%), iron (63.95%-68.65%), nonmetallic element boron and other additives such as dysprosium (0.6-8%), niobium (0.3-0.5%), aluminum (0.3-0.5%), copper (0.05-0.15%), etc.


Materiali magnetici molli per il settore elettronico
Come materiale magnetico molle, il ferro ad alta purezza presenta caratteristiche come la facilità di magnetizzazione, la demagnetizzazione, l'alta densità di induzione di saturazione e la bassa tensione. Viene ampiamente utilizzato nella produzione di vari apparecchi e dispositivi elettromagnetici, come relè elettromagnetici, motori elettrici e così via, e riguarda numerosi settori industriali, come l'aerospazio, l'industria automobilistica, la produzione meccanica, l'elettricità, l'elettronica e altri settori.
3. Soft magnetic materials used in the field of electronics
As a soft magnetic material, high-purity iron has the characteristics of easy magnetization, demagnetization, high saturation induction density, low tension, etc., and is widely used in the production of various electromagnetic equipment and devices, such as electromagnetic relays, motors, etc., involving many industries, such as aerospace, automobile, machinery manufacturing, electrical, electronic and other industries.